Overview
Acne is a common skin condition causing pimples and other abnormalities on the face and upper torso.
It is caused by a buildup of dead skin cells, bacteria, and dried sebum that blocks the hair follicles in the skin.
Bumps, such as blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, cysts, and sometimes abscesses, form on the skin, usually on the face, chest, shoulders, or back.
People of any age can experience this and most people have it at some time in their lives. Frequently, this occurs during puberty and in conjunction with a woman’s menstrual cycle due to an increase in hormone production.
Prevalence of acne
Acne of any severity usually lessens spontaneously by the early to mid-20s, but some people, usually women, have them into their 40s. Some adults develop mild, occasional, single lesions.
Acne can most often be managed simply by washing with a mild soap. However, if they are consistently large and painful, or has produced scars, treatment by a physician may be necessary.
Acne is the most common skin disease in the United States and affects 80% of the population at some point in life.
Our individuality or uniqueness as a person is the reason why some people experience these more severely than others. Homeopathy values this uniqueness of yours.
Do you know …
Vigorous washing and scrubbing may irritate the skin and can make acne worse.
There is no direct relationship between acne and inadequate face washing, masturbation, and sexual activity.
Even mild acne can be distressing, especially to adolescents, who see each pimple as a major cosmetic challenge.
Causes of acne
Acne is caused by an interaction between hormones, skin oils, and bacteria, which results in inflammation of hair follicles (the pores in the skin where hair grows). It is characterized by many types of skin abnormalities (lesions). They vary in size and severity, and some go deeper into the skin than others do:
- Blackheads (open comedones) – A blackhead develops if the blockage is incomplete.
- Whiteheads (closed comedones) – A whitehead develops if the blockage is complete.
- Pimples (inflamed closed comedones) – A pimple is an inflamed whitehead. The blocked sebum-filled hair follicle promotes the overgrowth of the bacterium Cutibacterium acnes (formerly called Propionibacterium acnes), which is normally present in the hair follicle. This bacterium breaks down the sebum into substances that irritate the skin. The resulting inflammation causes skin bumps that are commonly known as acne pimples.
- Raised, solid bumps (papules)
- Surface bumps containing pus (pustules)
- Deeper, firm bumps containing pus (nodules) – Deeper and more serious infections may result in hard nodules under the skin’s surface called nodules.
- Larger pockets containing pus (cysts)
- Sometimes even larger, deeper pockets containing pus (abscesses)
Both cysts and abscesses are pus-filled pockets, but abscesses are somewhat larger and deeper.
The skin contains many tiny hair follicles or pores. Each pore contains hair and a multi-lobed gland called a sebaceous gland which lies in the middle layer of skin (dermis) attached to the hair follicle. Sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum, which normally travels up the pore to lubricate the hair and skin. Acne results when a collection of dried sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria clogs the hair follicles, blocking the sebum from leaving through the pores.
The most common triggers of acne
- Puberty – It occurs mainly during puberty, when the sebaceous glands are stimulated by increased hormone levels, especially the androgens (such as testosterone), resulting in excessive sebum production. By a person’s early to mid-20s, hormone levels usually have decreased enough that it lessens or disappears. However, many women may have it into their 40s.
Other conditions that involve hormonal changes can affect the occurrence of acne as well:
- Pregnancy or menstruation – Acne may occur with each menstrual period in younger women and may clear up or substantially worsen during pregnancy.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome – Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormone disorder that can disrupt the menstrual cycle and can trigger or worsen acne.
- Certain drugs – The use of certain drugs, particularly corticosteroids and anabolic steroids, can worsen acne or cause acne flare-ups.
- Certain products applied to the skin – Certain cosmetics, cleansers, and lotions may worsen acne by clogging the pores.
- Too-tight clothing
- High humidity and sweating
Because acne naturally varies in severity for most people—sometimes worsening, sometimes improving—pinpointing the factors that may cause an outbreak is difficult.
Recurrent and severe acne can prevent people from doing what they usually enjoy and starts to affect the mind as well. They may become shy, depressed, and anxious. They may stop their activities, withdraw socially, and become preoccupied with their appearance. The mind-body complex is now fully affected and becomes a vicious circle which keeps an individual in suffering mode.
Symptoms of acne
Most acne occurs on the face but is also common on the neck, shoulders, back, and upper chest. Anabolic steroid use typically causes acne on the shoulders and upper back.
These can cause much emotional stress for adolescents and trigger social withdrawal.
There are three levels of severity:
- Mild – People with mild ones develop only a few non-inflamed blackheads or whiteheads, or a moderate number of small, mildly irritated pimples. Pustules, which resemble pimples with yellow tops, may also develop. Blackheads appear as small flesh-coloured bumps with a dark center. Whiteheads have a similar appearance but lack a dark center. Pimples are mildly uncomfortable and have a white center surrounded by a small area of reddened skin.
- Moderate – People with moderate ones have more blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and pustules.
- Severe – People with severe ones have either very large numbers of blackheads and whiteheads, pimples, and pustules or cystic (deep). In cystic acne, people have cysts that are large, red, painful, pus-filled nodules that may merge under the skin into larger, oozing abscesses.
Comparing Mild Acne and Severe Acne
Mild acne usually does not leave scars. However, squeezing pimples or trying to open them in other ways increases inflammation and the depth of injury to the skin, making scarring more likely. The cysts and abscesses of severe acne often rupture and, after healing, typically leave scars. Scars may be tiny, deep holes (icepick scars); wider pits of varying depth; or large, irregular indentations. Acne scars last a lifetime and, for some people, are cosmetically significant and a source of emotional stress. Scars may be dark.
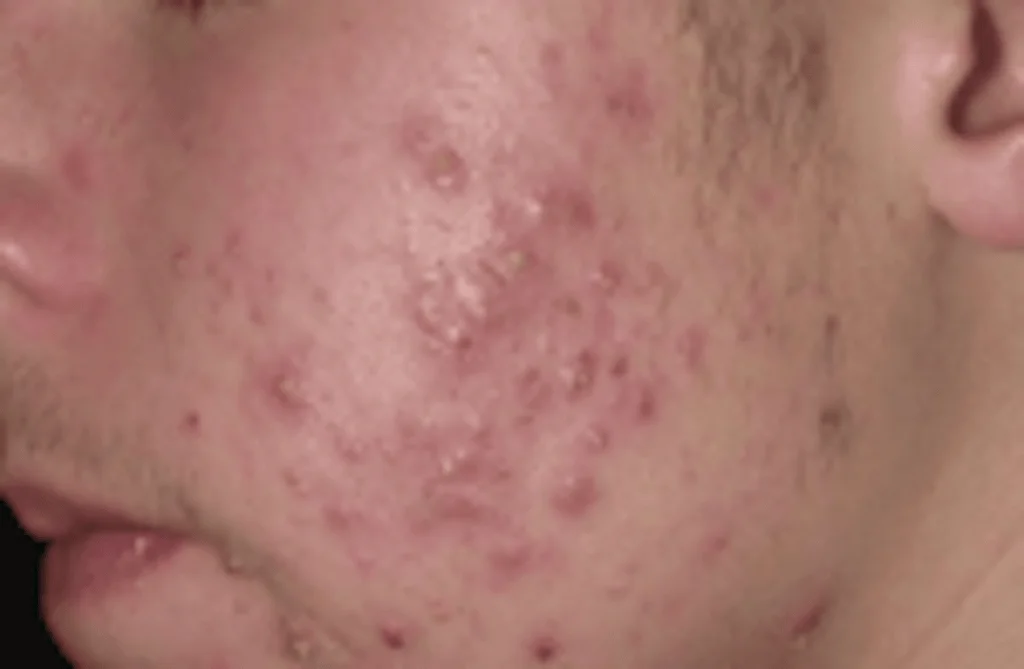
Examples of Acne
Acne conglobata is the most severe form of acne, causing severe scars and other complications resulting from abscesses. Severe acne can appear on the arms, abdomen, buttocks, and even the scalp.
Acne fulminans and pyoderma faciale (also called rosacea fulminans) are two possibly related and rare types of severe acne that typically occur suddenly.
Diagnosis of acne
A doctor’s thorough evaluation includes physical; mental; emotional; social health and environmental influence. Through this evaluation, doctors try to identify the causes, factors modifying it, and the impact of it on the daily life quality of a person.
Doctors base the diagnosis of acne on an examination of the skin. Doctors look for certain symptoms, such as blackheads or whiteheads, to determine that the person has acne and not another skin disorder, such as rosacea.
After the diagnosis is confirmed, doctors grade the severity of the acne as mild, moderate, or severe based on the number and type of lesions.
Doctors ask how the person feels; eats; sleeps and goes through a routine day. Identifying these changes is critical because they can make the situation better or worse and, if present, must be treated for it to be treated effectively.
Homeopathic Treatment of acne
After a thorough evaluation, each case is worked upon and a set of similar medicines is derived, from which one single medicine which fits the patient’s presentation at that time, in relevant intensity and repetitions is given.
Some need only one medicine throughout the duration of treatment and some need a few in sequence one after another across the treatment.
Counseling may sometimes be needed especially for those adolescents who see even single acne as a cosmetic challenge.
Timely follow-ups are essential to keep moving forward toward the goal of treatment and to identify, manage and overcome any obstacles to the outcome.

Outcome of Individualized Homeopathic treatment
With Individualised Homeopathic treatment focused on the person who is suffering, the outlook is as follows:
- Relieves emotional stress
- Reduces outbursts
- Improves sleep
- Reduces recurrence
- Relieves anxiety
- Relieves fatigue
- Restores function
- Better moods
- Improves quality of life
Each person is unique and hence the time taken for treatment and the results achieved are also unique.
Try to consult a well-qualified professional homeopath who practices adhering to the tenets of Hahnemannian Homeopathy for the Best Outcomes.